Due Dates
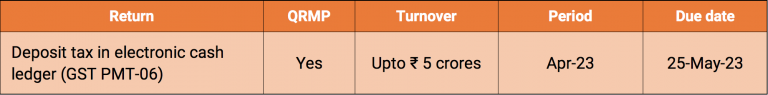
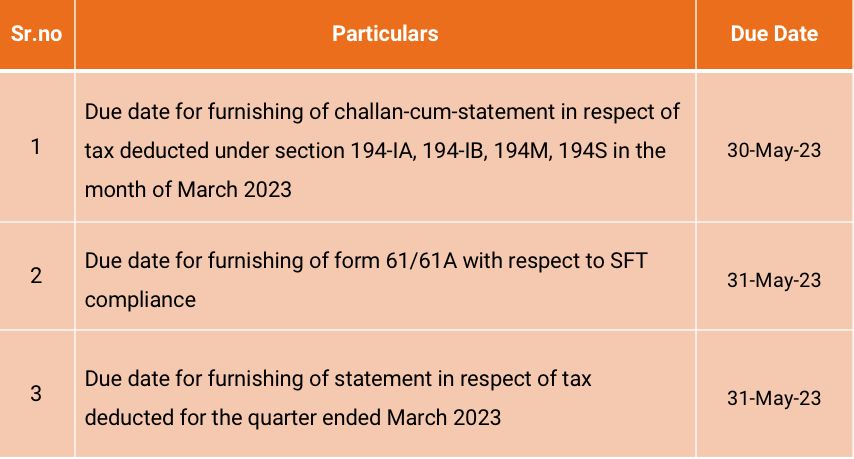
GST Compliance calendar for due dates falling in the month of May 2023
DIRECT TAX
Direct Tax Updates
Circulars/Notifications/Press Release
Employer to deduct tax as per new tax regime if employee didn't intimate about opting of old regime: CBDT.
- Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has issued clarification on the deduction of tax at source (TDS) by employers on the salaried income of the employee w.e.f AY 2024-25.
- The employer shall seek information from each employee regarding their intended tax regime and If the employee makes no intimation, the employer will deduct the tax following the new tax regime under section 115BAC.
CBDT notifies Cost Inflation Index for Financial Year 2023-24
- CBDT notifies Cost Inflation Index (CII) for FY 2023-24 at 348, as against CII of 331 for the preceding FY 2022-23.
Direct tax collection for FY 2022-23
- Provisional Collections FY 2022-23 exceeds union budget estimates by Rs. 2.41 lakh crore i.e 16.97%.
- Goss collection FY 2022-23 stands at Rs. 19.68 lakh crore showing a growth of 20.33% over FY 2021-22.
- Refunds of Rs. 3.07 lakh crore have been issued in FY 2022-23 which is increased by 37.42% from FY 2021-22.
Search and seizure of Co-operative Banks by Income Tax Department in Karnataka
- Income Tax Department commenced a Search & Seizure operation in the case of some Cooperative Banks, in the State of Karnataka, on 31.03.2023 and has resulted in seizure of unaccounted cash of over Rs 3.3 crore and unaccounted gold jewellery worth over Rs 2 crore. Further investigations are under progress.
Case Laws
Characterization of receipts earned by the assessee from borrowed funds: Gauhati HC
- Assessee, Brahmaputra Crackers and Polymers Limited received capital subsidy from Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers (“MoCF”) for setting up a specified project.
- Unutilized fund was temporarily parked in short-term deposits in Banks and interest was earned thereupon.
- Clarifications were received from the MoCF indicating that the interest earned from the temporary parking of such capital subsidy shall be treated as part of capital subsidy and the assessee accordingly claimed such interest income as capital receipts.
- Assessing Officer(“AO”) added such interest income under the head income from other sources.
- Assessee challenged the actions of the Assessing Officer to the Commissioner of Income Tax Appeal (“CIT (A)”) which ruled in favour of the assessee and Revenue filed an appeal against this before Tribunal.
- However, Tribunal dismissed the case and ruled in favour of the assessee.
No TDS benefit on salary foregone due to no actual payment: Delhi ITAT
- Assessee was working as Chief Manager and was removed from the services of the Bank.
- Assessee appealed before the High Court and Bank had deposited 46,70,066/- before the Hon’ble High Court in the form of Arrears of wages, Leave encashment, Gratuity dues, Monthly pension, Commuted value of pension of which on the basis of this settlement agreement Rs. 22,01,608/- was released in favour of the bank and 24,68,458/- was released in favour of the appellant.
- On the amount Rs. 22,01,608/- being forgone by the appellant, as per the terms of settlement, the entries of deduction made by the bank towards TDS of Rs. 11,06,499/- was also reversed.
- Assessee challenged the reversal of TDS stating that the salary foregone had been accrued.
- Assessee had argued as to applicability of the provisions of TDS he admitted that there is no liability to deduct TDS on accrual basis and TDS has to be deducted only at the time of payment.
- Tribunal was of the view that the foregone salary may after its accrual be chargeable to tax in the hands of appellant, but the appellant cannot claim that his employer should have deducted tax on the basis of accrual and the appeal was dismissed.
Sec. 54 relief cannot be allowed on basis of building permission plan submitted by assessee: Chennai ITAT
- Assessee, R Mohan during AY 2012-13 has sold his land and building for INR 1.20 crores and claimed benefit of indexation from the year property was inherited and took deduction u/s 54.
- Assessing Officer(“AO”) noticed that the assessee had computed indexed cost of acquisition by adopting Fair Market Value of the property as on 1-4-1981 contrary to the provisions of Sec. 49 of the Act.
- Therefore, AO re-computed cost of acquisition and allowed benefit of indexation from 2006 in which the assessee became absolute owner and also allowed deduction only to the extent of purchase of plot and not on the construction, since the assessee has submitted only the building plan, but not the evidence for construction.
- Commissioner of Income Tax Appeal (“CIT (A)”) confirmed the order of AO and assessee filed an appeal before Tribunal.
- Tribunal held that assessee had correctly taken the benefit of indexation and with regard to deduction u/s 54 it held that obtaining of building plan, estimate for construction is immaterial and the building should be constructed within 3 years.
Claim of ESOP expenses, remanded back to Commissioner of Income Tax Appeal (“CIT (A)”): Hyderabad ITAT
- Assessee is engaged in the business of trading in shares and securities as well as providing advisory services and is a subsidiary of Edelweiss financial services limited (EFSL).
- During the scrutiny assessment, the learned Assessing Officer disallowed the Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) cost claimed by the assessee as expenditure.
- Aggrieved by this assessee preferred an appeal before the learned CIT(A) and submitted detailed note along with case law stating that it had claimed deduction of the difference between the market price of EFSL shares as on the date of exercise by the employees and the grant price of such shares as expenditure under section 37(1) of the Act.
- Assessee placed reliance on the decision of the Hon’ble Apex Court in the case of in the case of CIT vs. Woodward Governor India (P) Ltd. 312 ITR 254 and other decisions in support of the contentions that incurring an expenditure by issue of shares at a price lesser than Fair Market Value could qualify as an ‘expenditure’ under the provisions of the Act.
- Learned CIT(A), however, observed that since the assessee failed to furnish the list of employees which indicated failure of the assessee to deduct the TDS and, therefore, under section 40(a)(ia) of the Act, 30% of the ESOP cost had to be disallowed and be added to the income of the assessee.
- The main argument of the Tribunal is that the order of the learned CIT(A) does not address any of the contentions raised by the assessee in their written submissions filed before the learned AO and CIT(A) should have given an opportunity to the learned Assessing Officer under Rule 46A of the Rules.
- Tribunal found it difficult to know the mind of the first appellate authority and hence set aside the order and restore the appeal to the learned CIT(A) for passing speaking order.
Expenses incurred with regard to any offence or which is prohibited by law is not deductible as an expense under IT Act: Jaipur Supreme Court?
- Assessee is an Individual who is engaged in the business of purchase and sale of Silver and search was conducted in his premises.
- Assessee was arrested u/s 104 of the Customs Act for committing offence punishable u/s 135 of the Customs Act.
- During search Assessing Officer(“AO”) proclaimed that certain items were not there in the books and passed an assessment order and made additions u/s 69A of the Income Tax Act.
- Assessee filed an appeal with the Commissioner of Income Tax (“CIT”) asking to allow the loss of silver as a business expenditure but however the CIT upheld the AO order, thereafter the assessee filed an appeal with the Tribunal.
- Tribunal held that any loss incurred by the way of expenditure by an assessee for any purpose which is an offence, or which is prohibited in law is not deductible as an expense and hence a penalty or confiscation is a proceeding rem (illegal in nature) and therefore any loss in pursuance of the same cannot by allowed as a deduction.
Company Law
Due Dates under the legislation
- Form 11 – Annual Return by Limited Liability Partnership – 30 May 2023
- Form DPT 3 – (Return of Deposit/Return of particulars of transactions by a company not considered as deposit) for the financial year ended on March 31, 2023 – 30 June 2023
- ECB 2 Return for the month ending April 2023 – 7 May 2023
Notifications / Circulars / Amendment issued during Apr / May 2020
MCA has vide Companies (Removal of Names of Companies from the Register of Companies) Amendment Rules, 2023, notification dated 17th April 2023 effective from 1st May, 2023, has introduced fast track closure of Companies via removal of name from Register.
Application for removal of name on accelerated Corporate Exit shall be taken up by the center specifically set up for this purpose. Certain procedural requirement for filing of application is also reduced. Accordingly, new Form STK 2, STK 6 and STK 7 are introduced.
Legal Updates
1. Amendment to Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021:
The Ministry of Electronic and Information Technology on 06 April 2023 has notified the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023.
Vide this amendment, the definition of “online game” has been inserted which means that “game offered on the Internet and accessible by a user through a computer resource or an intermediary” and “online gaming intermediary” means “any intermediary that enables the users of its computer resource to access one or more online games”.
As per the said amendment, if an online game can cause harm, the intermediaries shall inform the users of its computer resource not to host/ display/ upload/ modify/ transmit publish or store such game. The due diligence requirements as specified under Part B of the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 shall apply to online gaming intermediaries.
2. Introduction of the Competition (Amendment) Act, 2023:
The Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2023 assent of the Hon’ble President of India on 11 April 2023 to become the Competition (Amendment) Act, 2023 (“Amendment Act”). While the Amendment Act received Presidential assent on 11 April 2023, the provisions will come into force as and when the Central Government notifies the date of enforcement in the Official Gazette. The key amendments proposed by the Amendment Act are as follows:
- Introduction of the Deal Value Threshold: A new threshold pertaining to the deal value has been introduced for notification of combinations to the Commission. Any acquisition where the value of transaction, in connection with the acquisition of control, shares, voting rights or assets of an enterprise, merger or amalgamation exceeds INR 2,000 Crore shall be notified to the Commission, provided that the enterprise which is being acquired, taken control of, merged, or amalgamated has substantial business operations in India.
- Review period for the approval of combinations shortened: The Amendment Act aims at reducing the review timelines form 210 days to 150 days which can be extended to a maximum of 30 days for furnishing relevant information or to remove any defects by the parties to the transaction.
- Introduction of settlements and commitments: A settlement and commitment mechanism has been introduced to close investigations in a faster manner for violations relating to vertical agreements and abuse of dominance, however, cartels remain outside the purview of the settlement and commitment framework.
- A limitation period of 3 years has been introduced for filing an information before the CCI for any violation of the amended Act, including cartels. However, the CCI is empowered to condone delays.
SINGAPORE UPDATES
Latest Updates
Monetary Authority of Singapore
1) MAS Proposes Enhanced Safeguards for Prospecting and Marketing of Financial Products
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has published two consultation papers with proposals to enhance safeguards for prospecting and marketing of financial products. MAS’ proposals seek to enhance existing safeguards and introduce new measures to strengthen market conduct. particularly with the resumption of roadshows and the increasing use of social media and other digital media for prospecting and marketing activities.
The proposals regarding (i) prospecting activities at public places and via telemarketing and (ii) prospecting activities via digital applications and social media are separately set out in each of the two consultation papers. For physical prospecting at public places, the proposals include: making existing safeguards such as the disclosure of representatives’ identities and the financial institutions they represent mandatory, limiting the conduct of prospecting activities to commercial premises; requiring financial institutions to provide customers with additional time to consider whether to make a purchase, and limiting the use of gift offers which may influence decision-making. For digital marketing, the proposals include: strengthening controls over online advertisements to avoid misleading content, and tightening practices when appointing third party service providers to generate leads online.
It is proposed that amendments will be made to the Guidelines on Standards of Conduct for Marketing and Distribution Activities (“Guidelines”) issued by the MAS on 23 December 2016 to include new practices relating to prospecting activities at public places and that new Notices will be issued by MAS to legislate these enhanced safeguards following feedback on the consultations. The proposed safeguards for digital marketing are set out in draft Guidelines on Standards of Conduct for Digital Prospecting and Marketing Activities set out in the consultation paper. It is proposed that the new Notices and revised Guidelines for prospecting activities at public places and via telemarketing and the new Guideline on Standards of Conduct for Digital Prospecting and Marketing Activities will be effected six to nine months from their issuance date.
2) Singapore and China Establish Green Finance Taskforce to Strengthen Collaboration in Green and Transition Finance
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and the People’s Bank of China (PBC) have established the China-Singapore Green Finance Taskforce (GFTF). The aim is to deepen bilateral cooperation in green and transition finance between Singapore and China. Moreover, the GFTF will facilitate greater public-private sector collaboration. The aim is to work together to meet Asia’s needs as it transitions to a low carbon future. The GFTF’s inaugural meeting was hosted on 21 April in Chongqing. The parties discussed joint initiatives aimed at scaling up green and transition financing flows between Singapore, China and the region.
Singapore China GFFT priorities
• Taxonomies and Definitions. MAS and PBC will work together under the International Platform on Sustainable Finance (IPSF). The aim is to achieve interoperability between the Singapore and China taxonomies. They will collaborate subsequently to enhance the use of the IPSF’s Common Ground Taxonomy. In addition, there is a drive to deepen understanding of transition activities defined by China and Singapore.
• Products and Instruments. Singapore Exchange and China International Capital Corporation will establish a workstream to strengthen sustainability bond market connectivity between China and Singapore. This includes the issuances of and mutual access to green and transition bond products in China and Singapore.
• Technology. Metaverse Green Exchange and Beijing Green Exchange will establish a workstream that leverages technology to facilitate sustainable finance adoption. This includes piloting of digital green bonds with carbon credits.
The GFTF is co-chaired by MAS’ Assistant Managing Director (Development and International) and Chief Sustainability Officer, Gillian Tan, and Chair of the China Green Finance Committee, Dr Ma Jun. Members comprise senior representatives and sustainable finance experts from financial institutions and green FinTech companies from Singapore and China.
3) MAS Launches Finance for Net Zero Action Plan
Mr Lawrence Wong, Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Finance, and Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) Deputy Chairman, today announced the launch of MAS’ Finance for Net Zero (FiNZ) Action Plan at the opening of the Sustainable and Green Finance Institute of the National University of Singapore. The FiNZ Action Plan sets out MAS’ strategies to mobilise financing to catalyse Asia’s net zero transition and decarbonisation activities in Singapore and the region. It expands the scope of MAS’ Green Finance Action Plan launched in 2019 to include transition finance. Transition finance refers to investment, lending, insurance, and related services to progressively decarbonise areas such as power generation, buildings, and transportation.
The FiNZ Action Plan sets out MAS’ strategies to mobilise financing to catalyse Asia’s net zero transition and decarbonisation activities in Singapore and the region. It expands the scope of MAS’ Green Finance Action Plan launched in 2019 to include transition finance. Transition finance refers to investment, lending, insurance, and related services to progressively decarbonise areas such as power generation, buildings, and transportation.
The FiNZ Action Plan aims to achieve the following four strategic outcomes:
Data, Definitions & Disclosures. MAS will continue to promote consistent, comparable, and reliable climate data and disclosures to guide decision making by financial market participants, and safeguard against greenwashing risks.
o MAS has been working with the industry to co-create a code of conduct, which will require ESG ratings and data product providers to disclose how transition risks are factored into their products. A public consultation to gather wider feedback will be conducted in the second half of the year.
o MAS will work with relevant counterparts and stakeholders to enhance interoperability of taxonomies across jurisdictions, to catalyse cross-border green and transition financing flows.
o MAS has been working with the Singapore Exchange and other government agencies to set out a roadmap for key financial institutions (FIs) and listed companies to make International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB)-aligned disclosures on a risk-proportionate basis. MAS will partner with relevant bodies to build up companies’ capabilities in sustainability reporting.
· Climate Resilient Financial Sector. MAS will continue to engage FIs to foster sound environmental risk management practices and deepen climate scenario analysis and stress testing to identify climate-related financial risks. MAS will incorporate evolving international best practices in the supervision of FIs’ transition planning.
· Credible Transition Plans. To support FIs’ adoption of science-based transition plans, MAS will engage international partners such as the International Energy Agency to support the development of credible regional sectoral decarbonization pathways. FIs can reference these pathways when they set emissions reduction targets, and when they engage with their clients on initiatives to decarbonize their businesses.
· Green & Transition Solutions & Markets. MAS will promote innovative and credible green and transition financing solutions and markets to support decarbonization efforts and climate risk mitigation.
o MAS will expand the scope of its sustainable bond and loan grant schemes to include transition bonds and loans, with safeguards in place to mitigate the risk of “transition-washing” and ensure alignment with internationally recognised taxonomy and transition finance principles. To promote transparency in the sustainable debt market, MAS will incentivise the early adoption of entity-level sustainability disclosures by issuers or borrowers. MAS has set aside S$15 million over the next five years till end 2028 for the enhanced grant schemes. More details on these changes will be released shortly.MAS will extend the Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS) Grant Scheme till end 2025 to support the continued growth of catastrophe bonds and additional climate risk financing instruments such as sidecars and collateralised reinsurance arrangements. This will enable additional financing for protection against disaster risks to be raised from the capital markets. The S$15 million grant will defray the cost of issuing catastrophe bonds and the expanded suite of insurance-linked securities that focus on Asia risks.
o Building on past efforts, MAS will scale blended finance, in partnership with the private sector and philanthropic foundations, to mobilise financing for the decarbonisation of carbon-intensive sectors (e.g., managed phase-out of coal-fired power plants). In addition, we will support the development of carbon services and carbon credits markets in Singapore, to channel financing towards carbon abatement and removal projects in Asia.
https://www.mas.gov.sg/news/media-releases/2023/mas-launches-finance-for-net-zero-action-plan
Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore
1) Singapore and Brazil sign Protocol Amending the Agreement for Avoidance of Double Taxation
A Protocol amending the Agreement between the Republic of Singapore and the Federative Republic of Brazil for the Elimination of Double Taxation with Respect to Taxes on Income and the Prevention of Tax Evasion and Avoidance (DTA) and its Protocol (May 2018 Protocol) was signed on 17 April 2023 between the Government of the Republic of Singapore and the Government of the Federative Republic of Brazil.
The signing took place in Brazil between Singapore’s Minister for Foreign Affairs, Dr Vivian Balakrishnan, and Minister of Foreign Affairs of Brazil, Mr Mauro Vieira. This Protocol corrects minor translation discrepancies in the Portuguese text, specifically on Article 11 (Interest) of the DTA, and Paragraph 7 of the May 2018 Protocol.
2) GST: Clarification on "Directly in Connection With" and "Directly Benefit"
On 6 April, 2023, the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) published the Sixth edition of the e-tax guide (the “Guide”) on GST: Clarification on “Directly in Connection With” and “Directly Benefit”.
This e-Tax guide provides guidance on the interpretation and application of the two expressions, “directly in connection with” and “directly benefit” used in certain provisions on the zero-rating of services. “Directly in connection with” is used for services which have direct effect on goods or land. “Directly benefit” is used in the context of person(s) who derive direct benefits from the services.