CORPORATE LAWS
ECB 2 Returns for the month of June 2021 to be filed on or before 7 July 2021
MCA vide notification dated 15 June 2021 amended the Companies (Meetings of Board and its Powers) Rules 2014. As per this amendment Board Meetings may now be conducted through Video Conference for all matters without any restrictive provisions.
MCA vide clarification dated 23 June 2021 has extended time for holding Extra-ordinary General Meetings via Video Conference / other Audio Video means till 31 December 2021.
DIRECT TAX
Circulars/Notifications/Press Release
CBDT amends Rule 31A, prescribes new Annexure to Form 26Q
Notification No 71/2021 dated 8 June 2021
- Rule 31A is amended to include amounts and details on which tax is not deducted under Sections 194A, 194, 196D & 194Q.
- It also prescribes new annexures to Form 26Q (for TDS Return filing for non salary deductions).
CBDT issues guidelines for complete scrutiny of returns during FY 2021-22
Letter dated 10 June 2021
- Various parameters are prescribed for compulsory selection of returns for Complete Scrutiny during FY 2021-22 & conduct of assessment proceedings in cases pertaining to survey, search & seizure, notice u/s 142(1), escaped income, registration u/s 12A, 35 & 10(23C).
- The exercise of selection of cases to be completed by 30 June 2021.
CBDT notifies cost inflation index for FY 2021-22
Notification No. 73/2021 dt 15 June 2021
CBDT notifies cost inflation index as 317 for FY 2021-22 w.e.f. 1 April 2022 applicable for AYs 2022-23 onwards.
Functionality of Section 206AB and 206CCA
Circular No 11 of 2021 dt. 21 June 2021
CBDT issues Circular to notify a functionality called “Compliance Check for Sections 206AB & 206CCA” on the reporting portal of the Income-tax Department; The functionality would facilitate the tax deductor / collector to check if the deductee / collectee is a ‘specified person’ under Sections 206AB and 206CCA
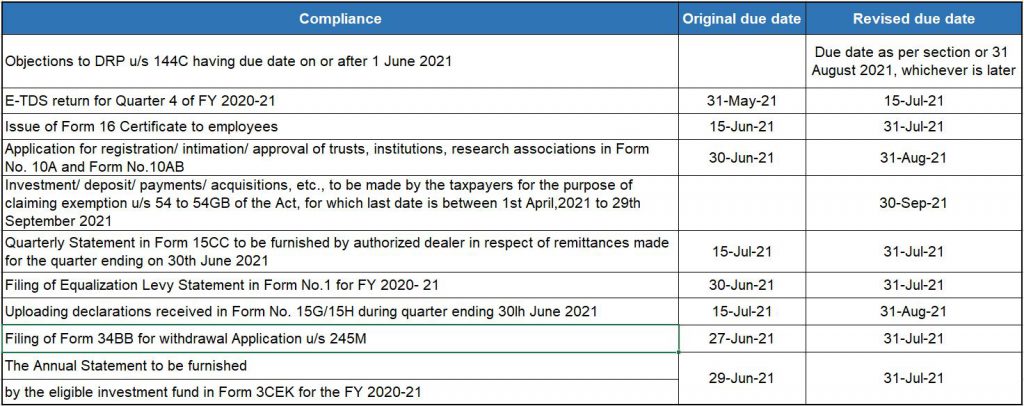
Relief provided by CBDT by way of extension of time limits of certain compliances in view of Pandemic
Circular 12 of 2021 dated 25 June 2021
Below are the extensions provided by CBDT in its notification:
Compliance Check Functionality for Section 206AB & 206CCA
Notification No. 01/2021 dated 22 June 2021
- The CBDT via notification No.1 of 2021 has stated the procedure to access and use the new functionality “Compliance Check for Sections 206AB & 206CCA“.
- Procedure has been laid out in the Notification.
CBDT notifies extension of due dates under Vivad se Vishwas Act
Notification No. 75/2021 dated 25 June 2021
- The last date for payment of the amount (without additional amount) to be paid under the VsV Act was previously extended to 30 June 2021 and is further extended to 31 August 2021.
- The date on or after which the additional amount shall also be paid under the VsV is further extended from 1 July 2021 to 1 September 2021.
- The “last date” for payment under VsV Act including the additional amount if any is 31 October 2021.
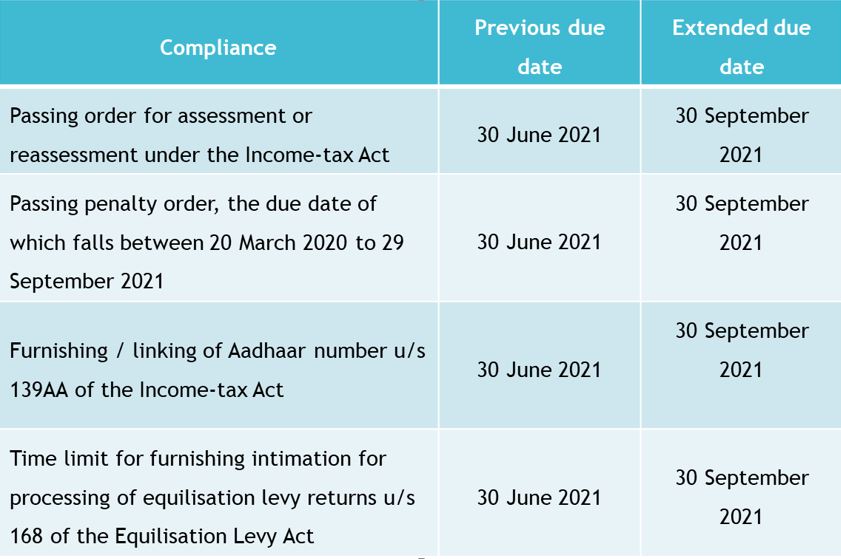
CBDT notifies extended due dates under the various statutes
Notification No. 74/2021 dated 25th June 2021
CBDT announces tax exemption for expenditure on Covid treatment and ex-gratia received on death due to Covid
Press Release dated 25 June 2021
- Income tax exemption on the amount received by a taxpayer form his employer or from any other person for medical treatment of Covid-19 during the period FY 2019-20 and subsequent years.
- Further, exemption on receipt of ex-gratia amount by the family members from the employer of such person (without any limit) or from other person (exemption shall be limited ₹ 10 lakhs in aggregate) on sudden death of the person on account of Covid-19 during FY 2019-20 and subsequent years.
- Legislative amendments will be proposed in the near future.
Clarification for use of functionality u/s 206AB and 206CCA
Press Release dated 22 June 2021
- The newly introduced sections 206AB and 206CCA require tax collection or deduction at a higher rate in case of certain specified persons.
- This would require the tax deductor/collector to satisfy himself that the deuctee/collectee is a specified person
- To ease compliance burden on tax deductor/collector, the CBDT has issued a new functionality “Compliance Check for Sections 206AB & 206CCA“.
- The tax deductor/collector can simply feed the PAN of the deuctee/collectee, and the functionality will respond whether the deductee/collectee is a specified person.
- This has to be done only at the beginning of the financial year without there being need of checking it again during the financial year.
CBDT issues guidelines for TDS on purchase of goods u/s 194Q
Circular No.13, dated 30 June 2021
The circular provides following clarifications on the applicability of section 194Q:
- Section 194Q shall not be applicable to transactions in securities and commodities carried out through recognised stock exchanges or cleared and settled by recognised clearing corporations including those located in IFSC.
- Section 194Q not to apply on transactions in electricity, renewable energy certificates and energy saving certificates traded through power exchanges registered in accordance with regulation 21 of CERC.
- It is clarified that that purchases from 1 April 2021, to 30 June 2021, to be included for the purpose of determination of threshold of ₹ 50 lacs for the previous year.
- Section 194Q will not be applicable to cases where buyer has either credited or paid the amount to the seller before 1 July 2021.
- Wherein amount is credited to the seller’s account, and in terms of the agreement / contract between the buyer and seller, the GST component is indicated separately; TDS u/s 194Q to be made on the amount credited without including GST.
- Wherein TDS u/s 194Q is made on payment to the seller, because payment is earlier than credit, TDS has to be made on the whole amount as it is not possible to identify that the payment with GST component of the amount to be invoiced in future.
- Since TDS u/s 194Q is made at the time of payment or credit whichever is earlier, tax would have been already deducted on purchase return, in such case if the money is refunded by the seller, then the amount of TDS made may be adjusted against next purchase from the same seller. No adjustment will be required if the purchase return is replaced by goods, by the seller.
- The provisions of section 194Q shall not apply to a non-resident whose purchase of goods from seller resident in India is not effectively connected with the permanent establishment of such non-resident.
- Section 194Q is not applicable in the cases where the seller’s income is entirely tax exempt and would apply where seller’s income is only partly exempt. Similarly, 206C(1H) would not apply to buyers who are exempt from income-tax. Like person exempt under section 10 or passed under special laws like RBI Act, ADB Act etc. However, this clarification would not apply if only part of the income of the person is exempt.
- It is clarified that since the provisions apply on payment or credit whichever is earlier, the provisions of section 194Q shall apply to advance payment made by the buyer to the seller.
- Section 194Q not to apply in the year of incorporation of the buyer as buyer is required to have gross receipts or turnover in excess of ₹ 10 Cr. in the financial year immediately preceding the financial year in which the transaction takes place.
- It is clarified that for the purpose of section 194Q, a buyer is required to have total sales or gross receipts or turnover from the business carried on by him exceeding ₹ 10Cr. during the FY immediately preceding the FY in which purchase of goods carried out. Hence, the sales or gross receipts or turnover from business carried on by him must exceed ₹ 10 Cr. His turnover or receipts from non-business activity is not to be counted for this purpose.
- If a transaction is both within the purview of section 194O (TDS on e-commerce operator) as well as section 194Q , tax is required to be deducted under section 194O and not under section 194Q.
- If a transaction is both within the purview of section 194-O as well as under section 206C(1H), tax is required to be deducted under section 194O
- If a transaction is both within the purview of section 194Q as well as under section 206C(1H), the tax is required to be deducted under section 194Q.
- Once the buyer has deducted the tax on a transaction, the seller is not required to collect the tax under section 206C(1H) on the same transaction.
- However, if for any reason, tax has been collected by the seller under section 206C(1H), before the buyer could deduct tax under section 194Q on the same transaction, such transaction would not be subjected to tax deduction again by the buyer. This concession is provided to remove difficulty, since tax rate of deduction and collection are same in section 194Q and section 206C(1H).
Case Laws
Pune ITAT: Directs treatment of bad-debts provision as non-operating expenditure for PLI computation; Remits computation
Honeywell Automation India Limited vs DCIT dated 3 June 2021
- The TPO rejected companies not having bad debts in their financials from the final set of comparables and also rejected assessee‟s argument of considering bad debt as non-operating.
- The ld. CIT(A) held that self-adjustment on account of excess bad debt couldn‟t be granted to the assessee and the ld. CIT(A) directed that self-adjustment for bad debts (by treating bad debts & bad debt provision as non-operating) could not be made to the profitability of the assessee.
- ITAT held that costs disallowed in return of income should be excluded from the cost base while computing PLI..
- Accordingly, ITAT remits the issue back to AO/TPO with a direction to treat the provision for bad debt as non-operating expenditure while computing assessee’s profitability, clarifies that the ad-hoc bad debts filter as applied by the TPO are liable to be rejected as well as directs inclusion of comparables having bad debt
Pune ITAT: Deletes TP-adjustment on payment of Management-fee
DCIT vs Spicer India Pvt. Ltd. dated 3 June 2021
- The assessee availed management services from its AE-Asia Investment Pvt. Ltd (AIPL) and applied CUP method for determination of ALP
- TPO rejected the same on the pretext that no evidences were submitted by the assessee to establish that the services were rendered by its AE and proposed TP-adjustment of ₹ 14.71 crores
- However, the CIT(A) deleted the impugned adjustment placing reliance on the order of this Tribunal with respect to deductibility of management expenses u/s 37 in the context of sec 92 of the Act) in assessee’s own case for AYs 2009-10 to 2014-15;
- The contention raised by the Revenue was that the CIT(A) had failed to appreciate that TP proceedings are different and the deductibility standards as applicable to Sec 37 cannot be applied for international transactions between AEs
- In earlier years, CIT(A) order was upheld stating that once commercial expediency of expenditure is established then the same is to be allowed as business expenditure;
- Following the same, ITAT upholds the CIT(A)’s order and deletes the impugned TP-adjustment
Agra ITAT: NFAC bound to follow HC exercising jurisdiction over Assessee' s AO
Mahadev Cold Storage vs Jurisdictional AO, Circle-4(1)(2), Aligarh. dated 14 June 2021
- NFAC made an adjustment by disallowing contribution received from employees towards ESI & EPF and deposited after due date but before the due date of filing of Income Tax Return.
- This was contrary to the law laid down by Allahabad HC in S C Sagun Foundry being the law of the land.
- CIT(A) passed the order relying upon a decision by Gujrat HC- not being the jurisdictional court.
- Assessee feeling aggrieved by the order passed by the CIT(A) National Faceless Appeal Centre, Delhi filed an appeal with ITAT, Agra.
- ITAT ruled that CIT(A) NFAC’s approach is incorrect & is against the scheme of the notification issued by the Board for creating the centralised NFAC and also against the settled principle of precedent.
Ahmedabad ITAT: Foreign nationals on deputation exclusively working for Indian AE, not supervisory or agency PE
Lubrizol Advanced Materials Inc., vs ACIT, Vadodara, dated 31 May 2021
- The assessee is a foreign company, based in USA. It has one associated enterprises (AE)- M/s LZAM India.
- The AE was in the process of establishing a new plant in India. For this purpose, the AE entered into Services agreement with the assessee wherein the AE was to pay actual cost-plus markup @ 10% to the assessee. As per DTAA, the assessee was treated as supervisory PE.
- The AO found that there were two employees namely Tim and Matt who were involved with the establishment of plant but their salary which was also partly reimbursed by the AE to the assessee was not considered in the income of the supervisory PE.
- The assessee submitted that Tim and Matt were Deputed individuals, working exclusively for the AE as directors and salary is paid after the requisite TDS in India. These are not the employees of the assessee and did not render any services to the assessee with respect to the supervisory PE in India.
- The ITAT ruled that there was no connection between the employees and the assessee which can establish the agency PE in India and also the salary paid will not be considered as income of the assessee.
Delhi HC: Sets aside faceless assessment, directs Revenue for granting personal hearing
Satia Industries Limited vs National Faceless Assessment Center, dated 31 May 2021
- The Assessment order was passed by NFAC without granting a personal hearing despite the fact that a general request was made.
- Aggrieved, Assessee filed a writ petition seeking stay on the operation of an assessment order, notice of demand and penalty notice.
- Assessee argued that it had made a request for personal hearing and also the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) under The Faceless Assessment Scheme, 2019 mandates the grant of personal hearing.
- Revenue’s appeal was that there was no clear demand for personal hearing.
- HC ruled that impugned orders cannot be sustained, and the consequential notices are set aside. The revenue shall grant a personal hearing to the assessee via video-conferencing mechanism after which a fresh order to be passed.
Mumbai ITAT: Assessment proceedings, once dropped, warrants reissuance of notice u/s 143(2) for altering returned income
IDBI BANK LTD vs Asst. CIT, dated 31 May 2021
- Assessee- IDBI Bank Ltd, filed return with loss of ₹ 155 crores for AY 2007-08 and the return was picked up for assessment.
- In the proceedings, it was found that ITR-V is not duly signed and verified. Accordingly, assessee physically submitted the ITR-V signed by Managing director.
- AO has not considered the latest ITR-V submitted and passed an order dropping the proceedings as the return is invalid. Also, assessee was not eligible to carried forward and made certain disallowances. CIT(A) upheld the AO order.
- Assessee preferred a revision application u/s 264 and CIT issued directions to AO to consider the return as valid. The AO passed an order treating the return as valid but restated the disallowances.
- In relation to order passed for dropping the proceedings by AO, the ITAT held disallowances in the said order “will have no legs to stand”
- In relation to order passed by AO incorporating CIT directions, ITAT held that AO shouldn’t have gone beyond the CIT’s directions and should have accepted the return filed without any adjustments. ITAT opined that for any disallowances, fresh notice u/s 143(2) and 142(1) should have been issued
Agra ITAT: Accumulated savings acceptable reason u/s 69A for cash deposit up to ₹ 2.5 Lacs by housewife on demonetization
Smt. Uma Agrawal vs ITO, dated 18 June 2021
- Assessee had deposited ₹ 2.11 lakhs into bank account for AY 2017-18 during demonetization period.
- Revenue made the addition of ₹ 2.11 lakhs u/s 69A r.w.s. 115BBE for reasons that a person with no sources of income could accumulate such amount and this was also upheld by National Faceless Appeal Centre.
- CBDT on 18 November 2016, issued a press release giving an exemption when the amount deposited by housewives is upto 2.5 lakhs, Revenue could not probe such cases.
- Thus, ITAT holds that since Assessee duly explained the source of deposit, it is for the AO to bring on record some cogent evidence to prove the amount deposited in the bank was undisclosed income arising from the business or from any other activities.
Mumbai ITAT: Errors in disclosing figures in Form 3CEB
Arysta Life Science India Limited vs ACIT, dated 21 June 2021
- The assessee had earned management fees of ₹ 1489.54 Lacs from two of its Associated Enterprises and the same was included in Financial Statements and considered in return of Income.
- However, in Form 3CEB, assessee has mistakenly reported the figure as ₹ 1002.13 Lacs.
- CIT(A) observed that assessee earned a management fee of ₹ 1489.54 Lacs and rejected the assessee submission that there was inadvertent and bona-fide error in reporting the correct numbers and enhanced the assessee’s income.
- ITAT held that amount of ₹ 1489.54 Lacs already forms part of assessee’s income and there is no concealment of income as alleged by Ld. CIT(A) in the impugned order. The figures in Form No.3CEB has been reported on ‘net basis’ which at the most, could be an inadvertent / bona-fide / oversight error.
Bombay HC: Grants ad-interim stay against assessment order passed without personal hearing
Credit Agricole CIB Services Pvt Ltd Vs DCIT dated 15 June 2021
- Assessee company filed return of income for AY 2017-18 and the return was picked up for assessment.
- Assessee company received show cause notice (SCN) cum draft assessment order under e-assessment proceedings and assessee has requested for personal hearing.
- However, revenue passed the assessment order, within a month after issuing SCN without granting the personal hearing computing total income at ₹ 21.13 Cr. As against returned income of ₹ 3.46Cr.
- Aggrieved by this, assessee filed a writ petition and was granted ad-interim stay directing the revenue not to take any action based on impugned order till the adjourned date of hearing.
Karnataka HC allows setoff of brought forward business loss against capital gains
Nandi Steels Limited Vs ACIT, dated 25 June 2021
Facts of the case:
- The Assessee, Nandi Steel Limited, carries on business of manufacture of iron and steel.
- The assessee had reported income from capital gains of ₹ 98,27,270 on account of sale of land and set it off against the brought forward business loss of earlier years to the extent of ₹ 39,99,652 in its return for AY 2003-04. return was duly processed, and refund issued.
- However, the assessment was re-opened under section 148 and the set off of business loss against capital gains was disallowed.
- Apart from the ground of validity under section 148, the assessee appealed the allowability of set off of business loss against the capital gains income before the CIT(A) and ITAT for which the ITAT made a reference for the setting up of a special bench. The special bench dismissed the assessee’s claim and disallowed the set off.
Assessee’s contention :
- The income has attributes of business income. Thus, even though the same is assessable to tax under a different head of income, it shall be eligible for set off with business loss.
HC Judgement:
- Sec. 72(1) employs the expression “under the head Profits and gains of business or profession” whereas clause (i) of Sec. 72(1) does not use the words “under the head”.
- Based on the thus, legal maxim “expressio unius est exclusio alterius” which implies that “expressed mention of one thing implies the exclusion of another”, the High court ruled that the “legislature has consciously left it open that any income from business though classified under any other head can still be entitled to the benefit of set off”.
- The HC placed its reliance on the SC ruling in GVK Industries and ruled the decision in favour of the Assessee.
Mumbai ITAT Allows write-off of investment in loss-incurring overseas subsidiaries as business loss
DCIT Vs Maneesh Pharmaceuticals Ltd, dated 17 June 2021
- Mumbai ITAT allows write-off of investments in overseas investments, incurring heavy losses, as business loss.
- Assessee had written-off investments made in two subsidiaries one in Europe and another in Africa as a result of accumulated losses over the years and claimed it as business loss.
- Revenue denied the business loss by treating the investment in subsidiaries as capital in nature whereas CIT(A) allowed write-off of investment in the Dutch (Europe) company but disallowed it for the Brazilian company by holding that there was no direct nexus of the investment and business of the assessee.
- ITAT finds that the investments were made in furtherance of business objectives and to earn revenue. It also noted that Assessee has earned export revenue from Africa unit in earlier years.
- The ITAT, while citing Karnataka HC’s ruling in ACE Designers, opines that it is a business loss and can be allowed as deduction thus ruling it in favour of the assessee.
Other Updates
USTR Announces, and Immediately Suspends, Tariffs in Section 301 Digital Services Taxes Investigations
- USTR announces suspension of tariff on goods for upto 180 days with six trading partners including India over Sec. 301 investigation on Digital Service Tax;
- It states that the investigations are meant to finally determine the imposition of additional tariffs on certain goods imported from Austria, India, Italy, Spain, Turkey, and the UK;
- Clarifies that the period of 180 days is provided as additional time to complete the ongoing multilateral negotiations on international taxation at OECD/G20;
- Expresses focus on finding “a multilateral solution to a range of key issues related to international taxation, including our concerns with digital services taxes” and a commitment for arriving at a consensus on international tax issues through OECD/G20
G-7 commits to 15% global minimum tax, equitable solution to taxing rights allocation
- G-7 communique commits to a global minimum tax of atleast 15% on a country by country basis and hopes for an agreement in July based on talks progressing on both pillars;
- The press release further talks of providing for ” appropriate co-ordination between the application of the new international tax rules and the removal of all Digital Services Taxes
- OECD Secretary-General welcomes G7 countries’ agreement on global minimum tax as landmark step
ITAT launches e-filing portal; Effective for Delhi Zone from June 21
ITAT Notice dated 4 June 2021
- ITAT launches e-filing portal in pursuit of delivering impartial, easy, and speedy justice;
- The portal has been developed for revised Memoranda of Appeal and Cross Objections and has been extensively tested for in-house and user acceptance;
- The portal will be soft-commissioned at Delhi Zone HQ w.e.f. 21 June 2021 and would gradually be rolled out across the country within a period of 4 weeks;
- The practice note, SOP, and FAQs has been made available in the public domain.
Goods and Services Tax
No penalty for non-compliance with Dynamic QR code up to 30 September 2021
With effect from 1 December 2020, B2C invoices issued by taxpayers having turnover more than INR 500 crores shall have Dynamic QR code. Subsequently, Government had deferred implementation of this Dynamic QR code requirement to 1 July 2021. Now vide Notification number 28/2021-Central Tax dated June 30, 2021 the Government has further deferred the said implementation to 1 October 2021 by way of waiver of penalty up to 30 September 2021.
Government extends period of IEC modification by one month
An IEC holder is required to update the details of his IEC registration electronically every year during the period April – June. In cases where there are no changes in IEC details, the same also needs to be confirmed online. For the current year 2021-22, this period is extended by one month up to 31 July 2021.
Due Dates
Important Due Dates July 2021
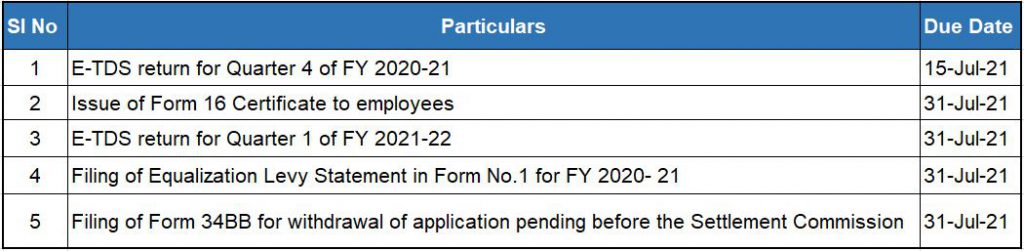
GST due dates 2021
Due dates for filing GST returns in the month of July 2021
With relaxation in interest rate for delay in GST payment
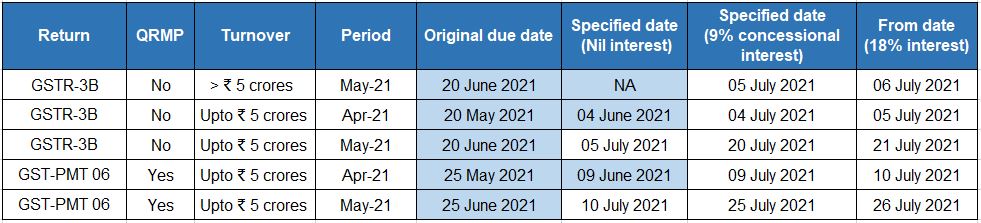
With relaxation in late fees for delay in filing of GST compliance returns
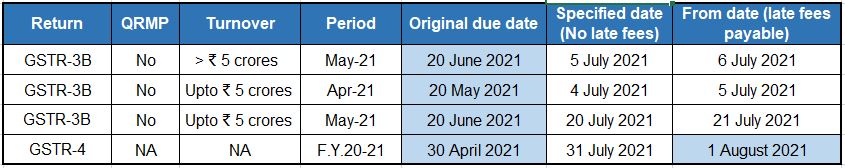
Without relaxation in late fees and interest
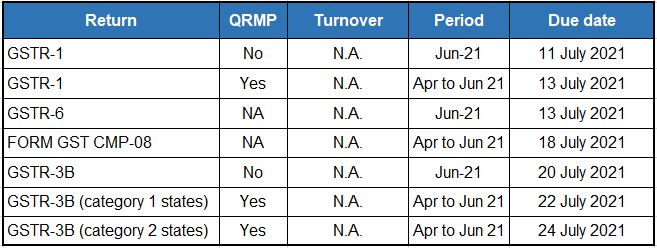
Category 1 States: Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, the Union territories of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands or Lakshadweep
Category 2 States: Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Uttarakhand, Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Assam, West Bengal, Jharkhand or Odisha, the Union territories of Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Chandigarh or Delhi
SINGAPORE UPDATES
1) Changes to the requirements for registration as a public accountant (PA) in the Accountants (Public Accountants) Rules (“Rules”)
With effect from 29 June 2021, the Accountants (Public Accountants) Rules will be amended to recognise the Chartered Accountants Program (CA Program) of the Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand (CA ANZ) as one of the accountancy qualification programmes that meets the professional examination requirement for PA registration. The amendment will allow individuals who have passed the CA Program on or after 1 January 2019 to apply for registration as a PA. This follows the reciprocal agreement entered into between the Institute of Singapore Chartered Accountants (ISCA) and CAANZ to mutually recognise the chartered accountancy qualifications of both bodies.
https://www.acra.gov.sg/docs/default-source/news-events-documents/2021/gazette_250621
2) Merger of the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA), Singapore Accountancy Commission (SAC), and Accounting Standards Council (ASC) Secretariat
The Ministry of Finance (MOF) will merge the accountancy-related units in the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA), the Singapore Accountancy Commission (SAC) and the Accounting Standards Council (ASC) secretariat into a strengthened accountancy function under one entity (henceforth referred to as “Merged Entity”). The ASC will remain as a Council appointed by the Minister for Finance.
The Government’s accountancy-related functions are currently housed in the following three entities: ACRA registers and regulates public accountants, business entities, and corporate service providers; SAC develops the accountancy sector and oversees the Chartered Accountant of Singapore (CA(Singapore)) designation, as well as its qualification programme – the Singapore Chartered Accountant Qualification (SCAQ) programme; ASC sets accounting standards for companies, charities, societies and co-operative societies.
This merger will strengthen effectiveness of regulation, standards-setting, and sector development by harnessing synergies across complementary functions. This will strengthen the Merged Entity’s ability to better develop and manage talent in a sustained manner, as well as provide better career development opportunities to officers.
The Merged Entity will be formed and will commence operations by the second half of 2022. The Merged Entity will retain the name Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA), which encompasses the enlarged functions of the Merged Entity, and is well-recognised by accountancy and business stakeholders. Mr Ong Khiaw Hong, Chief Executive of ACRA, will oversee the Merged Entity.
Monetary Authority of Singapore and Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore Updates
1. UK and Singapore mark a new era of Financial Services Cooperation
The launch of a new Financial Partnership was announced at the sixth UK-Singapore Financial Dialogue that was held virtually on 30 June 2021.
The Dialogue was chaired by Director General (Financial Services) of HM Treasury (HMT), Ms Katharine Braddick, and Deputy Managing Director (Markets and Development) of the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), Mr Leong Sing Chiong.
The Financial Partnership is supported by a new Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) which was signed by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, Mr Rishi Sunak, together with Senior Minister and Chairman of the MAS, Mr Tharman Shanmugaratnam. It demonstrates the joint commitment by the UK and Singapore to build a more comprehensive and enhanced relationship in financial services and strengthen regulatory cooperation between the two countries.
The Financial Dialogue discussed and agreed on the following areas of joint interest:
Regulatory cooperation: Both countries reaffirmed their commitment to effective regulatory and supervisory cooperation and to maintaining safe and open markets enabling participants to trade and manage risks more efficiently between their markets. The UK and Singapore discussed possible areas for enhanced collaboration, particularly in cross-border financial regulation. The UK will update Singapore on its new regime for marketing of overseas funds and its review of the Solvency II regime for insurance firms. The participants also discussed developments related to the global asset management industry, including the global norm of portfolio delegation, and agreed to maintain a dialogue on these developments.
Green finance and carbon markets: Accelerating green finance and encouraging the development of carbon markets remain a high priority for both the UK and Singapore.
Both countries will explore collaborating on a biodiversity pilot study, which will inform research into how nature-related risks will affect the financial system and contribute to this area of growing importance.
The UK and Singapore will encourage the private sector to explore ways to develop a transparent and robust voluntary carbon market for high quality voluntary carbon credits, such as deepening trading linkages and data sharing between Singapore and London to enhance inter-operability and cross-regional capital flows.
FinTech and stablecoins: The UK and Singapore had a productive discussion on recent technological developments and their respective regulatory approaches, including with respect to new payment methods and digital financial services, and agreed to continue sharing information. Both countries also discussed global developments and the evolving regulatory regime for stablecoins,and agreed to exchange regular updates on their respective regulatory approaches. The BoE presented highlights from its recently published discussion paper on new forms of digital money. Singapore outlined how its review on e-wallet payment limits has progressed and agreed to update the UK on the review. Both countries will continue to work together through the Global Financial Innovation Network (GFIN), and explore collaboration opportunities through their respective Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Innovation Hubs that are hosted in Singapore and London.
2. MAS Extends Training Support Measures to Foster Skills Development in New Growth Areas
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and the Institute of Banking and Finance (IBF) announced extensions to the enhanced training support measures to build capabilities and strengthen employability of the local workforce. These extended measures will be progressively reduced and cease on 1 July 2022.
Since the introduction of these measures in April 2020 and extension of training support (including the inclusion of deep-tech courses) in November 2020, training participation has increased over 60% year-on-year. Close to 500 financial institutions have tapped on these measures. While economic activities have progressively resumed and the financial sector has performed relatively well amidst the crisis, uncertainties remain in the economic environment. To ensure that financial institutions, FinTech firms and individuals continue to place emphasis on training and upskilling, MAS will extend the measures as follows:
- The course fee subsidies under the IBF-Standards Training Scheme (IBF-STS) and Financial Training Scheme (FTS) [1]will be extended by 6 months to 30 June 2022 with 80% of course fees subsidised, before returning to a more sustainable rate of 70% and 50% respectively from 1 July 2022.
- To help mature workers acquire industry-relevant skills as the industry transforms, Singapore citizens aged 40 and above will continue to receive the enhanced subsidy at 90% from 1 January 2022, for training under IBF-STS and FTS.
- The Training Allowance Grant (TAG) [2]will be extended for employees sponsored by financial institutions and FinTech firms by one year to 30 June 2022 at a rate of $10 per training hour.
The extensions will continue to support the training momentum in the financial services sector in new growth areas such as sustainable finance and family offices, and entrench the culture of training and upskilling as the sector transforms. MAS will continue to monitor the economic situation and review these measures accordingly.
3. MAS and Financial Industry Further Extend Support Measures for Individuals and SMEs in Tier 1 and 2 Sectors
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), together with the Association of Banks in Singapore (ABS) and the Finance Houses Association of Singapore (FHAS), has announced an extension of the existing industry-wide support measures for individuals and Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Tier 1 and 2 sectors that continue to face financial difficulties due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The industry-wide support measures introduced in 2020 have helped ease the financial strain of borrowers impacted by the pandemic. With the gradual opening up of economic activities, most borrowers have been able to resume loan repayments. However, as the COVID-19 restrictions have impacted borrowers unevenly, the extension is targeted at those individuals and businesses who continue to experience cashflow difficulties, by giving them additional time to transition to full loan instalment repayments.
The extension of support measures for individuals and SMEs is summarised below:
Ease cashflow and reduce debt for individuals who have sustained recent income/employment impact
The application window for the following support measures will be extended from 30 June 2021 to 30 September 2021:
- Property Loans: Reduced instalment repayment plans pegged at 60% of borrowers’ monthly instalment until 31 December 2021. A loan tenure extension of up to 3 years can also be discussed with lenders.
- Unsecured Revolving Credit Facilities: Convert outstanding balances to term loans at a reduced interest rate.
- Debt Consolidation Plans: Extend loan tenures by up to 5 years.
- Renovation and Student Loans: Extend loan tenures by up to 3 years.
Ease cashflow for Tier 1 and 2 SMEs that have sustained recent revenue impact
- The application window for the Extended Support Scheme – Standardised (ESS-S) will be extended from 30 June 2021 to 30 September 2021 for eligible SMEs in Tier 1 and 2 sectors.
- SMEs in Tier 1 and 2 sectors that are currently participating in the ESS-S may opt to defer 80% of principal payments on their secured loans granted by banks or finance companies, as well as loans granted under Enterprise Singapore’s (ESG) Enhanced Working Capital Loan Scheme and Temporary Bridging Loan Programme for an extended period till 30 September 2021.
- SMEs in Tier 1 and 2 sectors that have not participated in the ESS-S can also apply to their lenders to defer 80% of principal payments till 30 September 2021.
Facilitate restructuring of SMEs’ loans
- The application window for the Extended Support Scheme – Customised (ESS-C) will be extended from 30 June 2021 to 31 December 2021.
- SMEs with more than one lender may approach any of their lenders to assess if they would benefit from a multi-lender restructuring programme.
IRAS- Due dates
Form C-S/C for the FY 2020 -30-November-2021
Estimated Chargeable Income (ECI) (June year-end)- 30-Sep-2021
GST Return: April 2021 – Jun 2021- 31 July 2021