Company Law
ECB 2 returns for the month of March 2021 to be filed on or before 7 April 2021.
In terms of Companies (Management and Administration) Amendment Rules, 2021, a new format of Annual Return is being introduced for One Person Company and Small Companies with effect from 2020-21.
As per MCA notification dated 18 March 2021, the Central Government will establish a Central Scrutiny Centre for carrying out the scrutiny of Straight Through Process (STP) forms.
Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013 which provides for format of Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Account of a Company is amended to include more detailed disclosures and shall be effective from 1 April 2021.
In terms of Companies (Accounts) Amendment Rules, 2021 which will be effective from 1 April 2021, every Company maintaining its accounts in electronic form shall have software having feature of Audit trail of each and every transaction which shall create an edit log of each change made in the books of accounts along with the date to reflect when changes were made.
DIRECT TAX
Circulars/Notifications/Press Release
CBDT intends to offer relaxation against COVID-19 forced stay in India
Circular No. 02/2021 dated 03 March 2021
- CBDT issues Circular No. 2/2021 to address the issue of forced stay of individuals in India due to COVID-19;
- Prescribes Form-NR for examining whether any specific or general relaxation is required to provided to understand the situation of double taxation;
- Deadline to file Form-NR is March 31, 2021, required to be filed by individuals aggrieved of double taxation due to forced stay with PCIT (International Taxation);
- CBDT discusses domestic law, treaty law, and international experience on question of residential status for previous year 2020-21 due to forced stay that several individuals have faced in the recent past.
CBDT issues instructions for selection of cases u/s 148 for AYs 2013-14 to 2017-18
Letter to AO – 04 March 2021
- CBDT issues instructions for selection of cases u/s 148 by Jurisdictional Assessing Officer
- Directs that the following categories of cases shall be considered ‘potential cases’ for taking action u/s 148 by March 31, 2021 for AYs 2013-14 to 2017-18 –
(i) cases where there are audit objections (Revenue/Internal),
(ii) cases of information from any other Govt. agency/ Law enforcement agency,
(iii) Potential cases including –
(a) Reports of Directorate of Income Tax (Investigation),
(b) Reports of Directorate of Intelligence & Criminal Investigation,
(c) Case from Non-filer Management System & other cases as flagged by the Directorate of Income-Tax (Systems) as per risk profiling,
(iv) cases where information is arising out of field survey action and
(v) cases of information received from any Income-tax authority; Clarifies that “No other category of cases…shall be considered for taking action u/s 148..”; - Further clarifies that action u/s 148 shall be taken after forming a reasonable belief that income has escaped assessment and the reasons to believe shall be recorded and the required sanction u/s 151 shall be obtained;
- Appraises that these instructions do not apply to Central charges and International Taxation charges for which separate instructions are being issued.
CBDT clarifies, AO to give effect to DA's settlement orders under VsV
Circular No. 03 of 2021 dated 04 March 2021
- CBDT issues Circular to clarify that the Assessing Officer to give effect to the order passed by the Designated Authority under VsV.
- Based on the representation received from the field authorities, recognizes the absence of provision allowing Assessing Officer to pass orders consequent to settlement of tax arrears by the Designated Authority under VsV.
CBDT prescribes manner to compute annual accretion related to excess contribution made by employer to welfare funds
Notification 11 of 2021
- CBDT inserts Rule 3B in the Income-tax Rules for valuation of perquisite under Sec. 17(2)(viia); will come into effect from 1 April 2021;
- Prescribes formula for calculation of annual accretion by way of interest, dividend or any other amount of similar nature to the balance or to the credit of the fund or scheme on the amount contributed by the employer to:
(a) in a recognised provident fund;
(b) in the scheme referred to in sub-section (1) of section 80CCD; and
(c) in an approved superannuation fund. - TP= (PC/2)*R + (PC1+ TP1)*R
Approves Scientific Research Institution for section 35(1)(ii) & (iii)
Notification No. S.O. 1069(E) [NO. 12 /2021/ F.NO. 203/13/2019/ITA-II] Dated 9 March, 2021
- The Central Government approves M/s Bennett University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh having PAN: AAAJB1388A under the category of ‘University, College or other institution’ for Scientific Research and Research in Social Science and Statistical Research for the purposes of section 35(1)(ii) & (iii).
- This shall be deemed to have been applied for the assessment year 2020-2021 and shall apply with respect to the assessment years 2021-22 to 2024-25
CBDT notifies amendments in Form 12BA, Form 16 Part B and TDS return in Form 24Q
Notification No G.S.R. 170(E) dated 11 March 2021
- CBDT notifies following amendments in Form 12BA under Rule 26A(2)(b):
• Stock options allotted or transferred by employer being an eligible start-up referred to in section 80-IAC
• Contribution by employer to fund and scheme taxable under section 17(2)(vii)
• Annual accretion by way of interest, dividend etc. to the balance at the credit of fund and scheme referred to in section 17(2)(vii) and taxable under section 17(2)(viia) - In Form 16 Part B, new field to indicate whether employee has opted for concessional tax regime u/s 115BAC
- Notifies amended Form 24Q seeking aforesaid details
- The above new forms shall be applicable w.e.f. April 1, 2021
CBDT inserts Rule 114E(5A) for furnishing information on capital gains, dividend, and interest in SFT
Notification 16 of 2021- G.S.R 175(E) Dated 12 March 2021
- CBDT inserts sub-rule (5A) to rule 114E notifies the class of persons/ reporting persons to furnish a statement of financial transaction:
- Information relating to capital gains, dividend income, and interest income to be reported by:
♦ Recognized Stock Exchange
♦ Depository
♦ Recognized Clearing
♦ Corporation
♦ Registrar to an issue and share transfer agent - Information relating to transactions on dividend income to be reported by a Company
- Information relating to transactions on interest income to be reported by:
♦ Banking Company or a Co-operative Bank
♦ Postmaster General
♦ Non-banking financial company - It also defines the terms ‘listed security’, ‘mutual fund’, ‘recognised clearing corporation’, recognized stock exchange’ and ‘securities.
CBDT issues instructions for selection of international tax cases u/s 148 for AYs 2013-14 to 2017-18
Notification No. 17/ 2021 [F. No. 225/40/2021] / ITA-II Dated 15 March 2021
Instructions regarding selection of potential cases for issue of notice u/s 148 by International Taxation charge i.e. where income has escaped assessment for the remittances before 31 March 2017.
- The verification exercise for remittances which have been flagged by Directorate of Income tax (Systems) shall be conducted only where the flagged remittances made by a remitter is ₹ 5 crore or more and where it indicates there is any escapement of income.
- Following categories shall be considered as potential cases for the AY 2013-2014 to AY 2017-2018 for taking action u/s 148 by 31 March 2021:
♦ Cases where there are audit objections
♦ Cases of information from any other Government agency.
♦ Cases of information arising out of field survey action.
♦ Cases where information has been received any IT Authority including AO.
♦ Cases of non-filer management systems.
♦ Reports of Directorate of Income tax (Investigation), Directorate of Intelligence and Criminal investigation
♦ Cases of information arising out of FT and TR references
♦ Cases of information received from central charges after April 01, 2019, if not uploaded onto ‘VRU/CRIU functionality’ and flagged to jurisdictional authorities
- No other category of cases shall be picked other than above.
- The AO shall take the cases if he/she has reason to believe that income has escaped assessment.
CBDT notifies Rule 29BA and Form 15E to apply for certificate u/s 195 w.e.f. April 1
Notification No. 18/2021 F. No. 370142/24/2019-TPL, Dated 16 March 2021
- Rule 29BA – Application for grant of certificate for determination of appropriate proportion of sum (other than Salary), payable to non-resident, chargeable in case of the recipients:
- An application can be made by a person for determination of appropriate proportion of sum chargeable to tax for a non-resident for cases other than salary:
- The Assessing Officer shall examine the documents and determine whether the sum is chargeable to tax as per Income Tax Act r/w DTAA if any and if the sum is chargeable to tax the AO shall determine the appropriate proportion of such sum chargeable to tax.
- While examining, the AO shall consider tax payable on estimated income or assessed income of preceding four years, existing liability under the Income tax Act, any TDS, TCS or advance tax if any.
- Such certificate shall be valid for such period of the previous year as may be specified in the certificate.
- For making of such application, Form 15E has been introduced.
CBDT notifies Rules and applicable Forms supporting new procedure for registration and approvals
Notification No.19 dated 26 March 2021
- Further to provisions of the Income tax Act to provide for the registration/approval procedure of charitable, religious and other trusts, the Board (CBDT) has notified certain rules to effect the same along with the respective forms. These exemption/deduction provisions are in effect from April 01, 2021.
- The below points summarises the notifications,
♦ Rule 2C – Grant of approval of a fund, trust, university, medical/educational institute, or hospital u/s 10(23C);
♦ Rule 5CA – Intimation by company, research association, university, college or other institution u/s 35(1);
♦ Rule 11AA – seeking approval by institutions u/s 80G(5);
♦ Rule 17A – registration of a charitable or religious trust or institution u/s 12A;
♦ Rule 18AB – furnishing statement of particulars and certificate u/s 35(1A) and 80G(5) to the authorities and donors, respectively by concerned entities; - The rules contain requirements and conditions to be fulfilled for claiming exemptions and prescribe the procedure to be complied with along with applicable forms.
CBDT clarifies the provisions of the Direct Tax Vivad se Vishwas Act, 2020
Circular No. 4/2021 dated 23 March 2021
- On receiving several representations, the CBDT issued circular no. 4/2021 dated 23 March 2021 clarifying the classification of a case as a ‘search case’ for the purposes of Vivad se Vishwas Act.
- In order to remove any uncertainty with respect to the above regard, it is hereby clarified that a ‘search case’ means an assessment or reassessment made under sections 143(3)/ 144/ 147/ 153A/ 153C/ 158BC of the Income-tax Act in the case of a person referred to in section 153A/153C or section 158BC/158BD of the Act on the basis of search initiated under section 132, or requisition made under section 132A of the Act.
CBDT further extends reporting under clause 30C & 44 of Form 3CD until 31 March 2022
Circular No. 5/2021 25 March 2021
- The reporting under clause 30C and clause 44 of Tax Audit report (i.e., Form 3CD) was kept in abeyance till 31 March 2021 vide circular no. 10/2020 dated 24 April 2020.
- Due to the situation of COVID-19 across the country, CBDT extends the suspension of these reporting requirement under clauses 30C and 44 of Form 3CD to be kept in abeyance until 31 March 2022 vide circular 10/2021 dated 25 March 2021.
CBDT clarifies the time for disposal of condonation of delay in Form 10BB
Circular No. 6/2021 dated 27 March 2021
- As per Rule 16CC, the audit report of accounts of certain funds/ trust/ institution/ university/ educational or medical institution/ hospital is to be furnished in Form no. 10BB electronically along with returns to claim exemption u/s 10(23C) of the Act.
- As per representations received before for AY 2016-17 and onwards the CBDT, had issued circular no. 19/2020 that it may condone delay in filing of the form and directed the authorities to accept applications for such condonation and dispose the same by 31 March 2021.
- However, with circular no. 6/2021 dated 27 March 2021, the CBDT has amended the deadline for such disposal to be 3 months from the end of the month of receipt of such application.
CBDT clarifies the time for disposal of condonation of delay in Form 10B
Circular No. 7/2021 dated 26 March 2021
- Section 12A of the Act, provides that a trust or an institution having total income (before giving effect to Sec 11 and Sec 12) exceeding the maximum amount not chargeable to tax, should furnish audit report of accounts in Form no. 10B electronically along with returns to be entitled for exemption u/s 11 and 12 of the Act.
- As per representations received for years prior to AY 2018-19 CBDT, had earlier issued circular no. 10/2019 authorizing ITO to accept a belated audit report after recording reasons in cases where some delay has occurred for reasons beyond the control of the assessee.
- Such application was earlier required to disposed by 31 March 2021. However, with circular no. 7/2021 dated 26 March 2021, the CBDT has amended the deadline for such disposal to be 3 months from the end of the month of receipt of such application.
Case Laws
ITAT: Uber India, mere remitter to driver-partners of Uber BV; Not liable for TDS u/s 194C
ITA No.5862 & 5863/Mum/2018 Uber India Systems Private Limited vs JCIT, Mumbai dated 4 March 2021
- Mumbai ITAT holds that Uber India (UISPL, assessee-company) cannot be held as ‘assessee-in-default’ for non-deduction of tax u/s 194C in respect of payments made to drivers on behalf of Uber B.V. for AY 2016-17 and 2017-18;
- Revenue held Uber B.V. was providing transportation services and the payments made to its driver-partners was liable to TDS u/s 194C
- Further, Revenue held that since assessee company was the face of Uber BV in India, which collected the payments from users and remitted the same to the drivers, it was thus the ‘person responsible for making payments’, liable to deduct tax at source u/s 194C;
- Holds that assessee-company cannot be held as ‘person responsible for making payments’, explains that “the role of UISPL is limited to act as a payment and collection service provider of Uber B.V. whereby the ride fare is collected by UISPL in its bank account on behalf of Uber B.V. and thereafter payments are made, on the instruction of Uber B.V., to Driver-Partners.”;
- Refers to Sec. 204(iii) and states that in the instant case assessee is not payer of money but only the remitter which is collected from the users on behalf of Uber B.V., as it entered into contract with driver-partners and not the assessee;
- Further refers to various clauses of agreement between Uber B.V. and driver-partners and Uber BV and Users to conclude that “Uber B.V. is involved in rendering lead generation service to the Driver-Partner and transportation service is not provided by Uber B.V. or UISPL.The transportation service provided by the Driver-Partner to Users is a contract between them to which Uber B.V. is not a party. Therefore, it is clear that UISPL is not a part of the contract and no payment obligation is imposed either under the agreement with the Driver-Partner or under the agreement with the User.”
Exclusion of comparable for software-developer applying turnover-filter
Microchip Technology (India) Pvt. Ltd vs DCIT, Circle-4(1)(2), Bangalore Dated 9 March 2021 (Hon’ble Bangalore ITAT- IT(TP)A No.1498/Bang/2017)
- The Assessee in engaged in the business of provision of Software Development Services (SWD services) to its wholly owned holding company.
- The assessee selected Operating Profit/Operating Cost (OP/OC) as the Profit Level Indicator (PLI) for the purpose of comparison which was arrived at 16.59% in its TP study.
- The TPO accepted TNMM as the MAM and also used the same PLI for comparison. However, he selected his own 7 companies as comparable and made an adjustment based on it.
- The Assessee adjudicated only on the turnover filter ground for removal of 5 companies as and all other grounds would be academic, hence need not be adjudicated.
- The ITAT relied on coordinate bench ruling in case of Autodesk India Pvt Ltd, wherein turnover filter was held as an important criteria for choosing comparable and companies not meeting turnover filter of ₹ 1-200 crores were excluded.
- Following aforementioned ruling and thereby applying the turnover filter, ITAT accepts Assessee’s plea and excluded 5 comparables, on account of having turnover of more than Rs 2,000 crores than Assessee’s turnover of Rs. 119.38 crores
Investments in India by non-resident through remittance from abroad, non-taxable
Mr. Iqbal Ismail Virani Vs ITO (International Taxation), Ward-1, Panaji Dated 12 March 2021 (Hon’ble Panaji ITAT- ITA No.187/PAN/2019)
- The Assessee was a NR in India for last 30 years. During the year under consideration, the Assessee made investments (purchase of properties) through remittance received from his foreign Bank account.
- The AO held the investments to be unexplained cash credits and made addition u/s 68/69 of the Act disregarding Assessee’s submission that investment was made from the sale proceeds of gold bars in Dubai and out of maturity proceeds of FDs of company owned by assessee in Dubai.
- ITAT explains that the question of assessing such remittance to tax arises only when there is no evidence to show that the amounts are in fact remittances from abroad. In this case there was ample evidence in the form of confirmation letter from Bank of Baroda in Dubai w.r.t maturity proceeds of FDs, invoices supporting sale of gold bars in Dubai and copies of cheque issued in favour of assessee.
- ITAT held that the remittance received from Assessee’s bank account in Dubai to his SBI account in Goa or remittance to the vendors of the properties is neither income received or deemed to be received in India nor was accrued or arisen or deemed to be accrued or arisen in India, therefore, the question of chargeability to income tax in India does not arise.
Delay in realization of AE-receivables separate international- transaction, imputes interest cost
M/s. Doosan Power Systems India Pvt. Ltd. IT(TP)A No 5/Chny/2018 AY 2011-12
- The assessee is engaged in the business of engineering design and related services to its overseas group companies.
- The assessee’s contention that delay in realization of receivables is not a separate transaction for the AY 2011-2012. ITAT notes that as per the amendment in section 92B, the delay in realization of receivables from AE beyond credit period constitutes a separate international transaction w.e.f. from AY 2013-14 onwards. The amendment shall have a retrospective effect.
- ITAT also mentions that the amendment of clause (c) of section 92B i.e. realization of receivables would tantamount to indirect funding to AE.
- ITAT also states that merely because there is no interest clause in the agreement or the assessee doesn’t pay any interest to associated enterprise, the revenue cannot be deprived of their legitimate share.
- Accordingly, it directs the assessee to apply LIBOR+300 basis points as the appropriate rate for imputing interest on overdue receivable.
New source of disallowance cannot be introduced in appellate proceedings; Deletes addition
Shri Shivji Amba Gami ITA No 6651/Mum/2018 AY 2014-15
- The assessee is an individual and is engaged in the business as builder and developer.
- During AY 2014-15, the assessee had sold eight flats at loss. The AO during assessment added back the differential amount (Stamp Value – Sale Consideration) of ₹ 6,83,500/- u/s 43CA.
- In the said case, CIT(A) had accepted that Section 43CA was not applicable to the case as section 43CA was introduced into the statute by Finance Act, 2013 w.e.f. 1 April 2014.
- However, the CIT(A) had made certain additions on account of differences between sale consideration and stamp duty value on various other grounds such as loss of assessee in respect of housing project, doubting the genuineness of expenditure incurred and sale of other flats at higher rates.
- The ITAT states that CIT(A) has gone into completely new arena by introducing a new source of disallowance during appellate proceedings since the same was never a part of assessment proceedings.
- Also, ITAT opines that “Without making any enquiry or bringing material on record to establish the fact that the assessee has received any amount over and above the declared sale consideration, no addition could have been made when it is accepted that section 43CA meant for such deemed addition, is not applicable to the subject transaction.”
Holds no negative working-capital adjustment for captive service provider;
M/s. IDS Software Solutions India Pvt. Ltd. IT(TP)A No 84/Bang/2017 AY 2012-13
- The assessee is engaged in the business of software development services in the field of leasing, loan accounting and portfolio management solutions.
- One of the ground raised by the AR relates to consideration of negative working capital while making Transfer Pricing adjustment. It is the plea of the assessee that the negative working capital should be ignored.
- ITAT directs TPO not to make negative working capital adjustment, relying on coordinate bench ruling in e4e Business Solutions India P Ltd wherein it was held that negative working capital adjustment is not required in the case of a captive service provider as it has no borrowings and is fully compensated by the parent on a total cost plus. The assessee has no working capital risk – in other words, it is a risk-insulated service provider to the parent.
- As mentioned by the OECD, comparability adjustments should not be performed on a routine or mandatory basis but rather on a case-by-case basis depending on the facts and circumstances. Economic rationale of Working capital of a business is the capital used in its day-today trading operations. Working capital is affected by numerous business incidences. It is very common for tested party and each of the potential comparables to differ materially in the amount of working capital
Ahmd ITAT: Sec. 206AA not above beneficial treaty provision; Approves 10% TDS on remittance to Czech Republic
Jyoti Limited Vs DCIT ITA No.666/Ahd/2018 22 March 2021
Ahmedabad ITAT allows assessee’s appeal to affirm TDS @10% as per DTAA to be correct
Facts of the case:
- The Assessee, Jyoti Limited, withheld taxes @ 10% on payments made to a company resident in Czech Republic. The TDS was as per the rate in Article 12 of the relevant DTAA. However, the Revenue contended for a higher rate of 20% for not furnishing PAN as per section 206AA.
- The Assessee relied on SC Judgement in the case of Azadi Bachao Andolan & Anr. reported in 263ITR 706(SC) & also the Circular No. 333 dated 02.04.1982 issued by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) stating that “where a double taxation avoidance agreement provides for a particular mode of computation of income, the same should be followed, irrespective of the provisions in the Income-tax Act.”
Conclusion:
- Ahmedabad ITAT stated that section 90(2) of the Act provides that DTAA would override the provisions of the Act, if they are more beneficial & accordingly a lower rate as per DTAA would apply over the higher rate of 20% under section 206AA of the Act.
Bang ITAT: Upholds re-characterization of reimbursement as provision of intra-group services
Tata Coffee Limited Vs DCIT IT(TP)A No.190/Bang/2015 22 March 2021
Bangalore ITAT defends revenue in re-characterising reimbursement as intra-group service
Facts of the case:
- The Assessee, Tata Coffee Limited, intending to acquire an overseas company, incurred expenses on carrying out due-diligence services. However, the plan got shelved and another AE of assessee acquired such company, and the assessee charged the due-diligence expenses to such AE on actual cost basis, as “Reimbursement of Expenses”.
Conclusion:
- Earlier the TPO overlooked the nomenclature of ‘reimbursement’ and considered Nil expenditure under CUP method and made a TP adjustment. In further appeal, the DRP confirmed a Markup restricted to 10% based on operating profit.
- The Bangalore ITAT agrees with DRP observation that in a similar uncontrolled transaction, the assessee would have charged a mark-up in the normal course since its resources, infrastructure, skills, time, etc. were invested.
- Contention of assessee that the transaction would fall outside the scope of TP provisions in the absence of any income element was not accepted.
Bangalore ITAT rules on comparable for Software and Marketing Segment
Salesforce.com India Pvt. Ltd. Vs DCIT IT(TP)A No.3286/Bang/2018 22 March 2021
Bangalore ITAT rules on comparable selection in respect of assessee’s software development services (SWD) segment and marketing and sales support services (MSS) segment and remits the issue back for TP adjustment on account of interest on outstanding receivables.
Facts of the case:
- The Assessee, Salesforce.com India Pvt. Ltd., renders services to AE under contract and had delay in collection of receivables. ITAT excluded certain companies as comparable in SWD segment owing to their significant intangibles, unavailability of segmental details, huge turnover, high brand value leading to a high bargaining power in the market, etc.
- While ITAT accepted assessee’s pleas to exclude comparables in MSS segment citing extraordinary event of amalgamation, functional dissimilarity and earning income from other diversified activities.
Conclusion
- ITAT relies on Special Bench ruling in Instrumentation Corporation wherein it was held that outstanding sum of invoices is akin to loan advanced by assessee to foreign AE, hence it is an international transaction as per explanation to Sec. 92B
Chen ITAT: Holds fees paid to lawyers, CAs outside India not FTS but Business Income - Deletes disallowance u/s Sec.40(a)(i)
Sundaram Business Services Ltd Vs ITO ITA No.771/CHNY/2019 19-03-2021
Chennai ITAT deletes disallowance w.r.t. legal and professional fees paid to non-resident without TDS u/s 195 holding them as non-taxable as FTS or business income
Facts of the case:
- The Assessee, Sundaram Business Ltd., paid professional fees to a law firm in Australia and also to a CA entity in US for services rendered, without TDS u/s 195. The revenue also disallowed u/s 40(a)(i), the provision made for such professional charges.
Conclusion:
- ITAT noted that legal charges paid to law firm in Australia was covered under Article 14 of the India-Australia DTAA whereby independent professional services by a firm shall be taxable only in that State where firm is a resident, unless it has a fixed base in India.
- Further, fees paid to CA entity in US is covered in Article 7 and not in Article 14 of India-USA DTAA. However, it did not have any PE in India for such services being rendered outside India. Also, such nature of services is neither in by way of royalties as defined u/s 9(1)(vi) nor FTS because the entity do not make available technical knowledge, expertise, skill, know-how or processes to the assessee. Hence not liable to TDS u/s 195.
Pune ITAT holds branch reimbursement to HO not liable to TDS
BYK Asia Pacific Pte. Limited Vs ACIT(IT) ITA No.2110/PUN/2019 24 March 2021
Pune ITAT lays twin conditions to classify payment as ‘reimbursement’, for TDS u/s 195
Facts of the case:
- The Assessee, BYK Asia Pacific Pte. Limited, a tax resident of Singapore operates through branches in many countries including Indian BO, which is PE of Singapore HO.
- Assessee provides technical support services to its German Parent company, and the service fees is reimbursed by Singapore HO with 10% markup, taxed in India. During the course, Indian BO reimbursed its HO for expenses incurred on its behalf without TDS.
Conclusion:
- The ITAT holds that 2 fundamental conditions must co-exist in order to fall within the domain of ‘reimbursement’, i.e.,
♦ one-to-one direct correlation between the outgo and inflow must be established,
♦ receipt and payment must be of identical amount;
- ITAT remarks that “receipt of a fixed amount, which may be more or less than the actual outgo, cannot be designated as reimbursement” and allows deduction of expenses towards IT, seminar, training, printing and staff welfare to assessee.
Del ITAT: CSR provision without 'certainty' on end use, to be unascertained liability for MAT
Delhi ITAT holds that provision for CSR expenditure made by assessee is an unascertained liability, liable to be added back for computation of book profits u/s 115JB
Facts of the case:
- The Assessee, Pawan Hans Limited, a Public Sector Company, created a provision for CSR expenditure, as prescribed under Companies Act, 1956 read with the guidelines laid down by the Department of Public Enterprises, and contended that the provision was an ascertained liability.
Conclusion:
- Delhi ITAT observes that the provision for CSR expenditure has been quantified in accordance with the required guidelines but how the amount will be spent has neither been determined nor has been specified by the assessee.
- Further, ITAT opines that it is just an amount which has been set aside for being spent towards Corporate Social Responsibility but without any further certainty of its end-use. Further states that, how the amount ear-marked for spending towards the CSR obligation will be spent is “not certain”, “clear” or “definitely known”.
- Therefore, it cannot be said that the liability is an ascertained liability. Thereby, ITAT dismissed Assessee’s appeal.
Corporate Gossip
ITD conducts searches in Jharkhand
22 March 2021
The Income Tax Department carried out searches on a closely-held Group in Jharkhand on 17 March 2021 and concluded the same on 20 March 2021. Search and survey was carried out at more than 20 premises.
Allegations:
- Engaged in manufacturing and trading of Sponge Iron, MS Ingots, MS Rods & TMT bars, the Group has dealerships of petrol pumps as well.
- It indulged in business outside the books while ploughing back the unaccounted income into the Group in various forms including investments in properties and expensive personal items.
Discoveries:
With all the efforts the Department succeeded to spill the beans by uncovering:
- 100 crores as share capital at excessive premiums via shell companies
- 25 crores by way of unsecured loans
- 30 crores from bogus commodity profit entries
- 3.07 crores of unaccounted cash held
- 1.28 crores of unaccounted bullion and jewellery seized
ITD raids Mumbai based Mobile importers
20 March 2021
- Adding on to the multiple surveys and raids conducted across India, the Income Tax Department also searched and surveyed as many as 29 and 14 premises in Mumbai respectively.
- The transactions involved included sale of properties to develop commercial malls exclusive for mobile accessories business, established to undertake group imports from China and sell across India with under invoicing and payment policy routed through hawala channels and stored in 13 secret Godowns.
- Although further investigations and exercises are in progress, but with all the evidences obtained so far, the Department managed to unearth unaccounted receipts and investments of around ₹270 crores.
- The transactions with the Chinese counterparts were undertaken through We-Chat App and were recovered using forensics.
Other Updates
Other updates and news
- Vide Notification No. G.S.R. 162(E) [NO. 13/2021/ F. NO. 142/15/2015-TPL] Dated 09 March 2021- CBDT amends Rule 10V for computation of remuneration payable to fund manager u/s 9A by including two addition proviso.
- Vide instruction F. No. 414/132/2018-IT (INV.I)(PART I) Dated 9 March 2021- CBDT issues FAQs on general action required to be taken in cases where income escaping assessment pertains to assessment years 2013-14 to 2017-18.
- Vide Letter to AO dated 12 March 2021: CBDT issues certain instruction regarding to selection of cases for issue of notice for reopening of assessment u/s 148. This is clarification to the CBDT’s letter dated 4 March 2021.
- For around 2.68 lakh IT forms, UDIN’s have not been uploaded by Chartered Accountants on the IT portal. In order to mitigate the likely hardships that would be faced by the taxpayers due to non-compliance, all the missed UDINs between the period 1 February 2019 to 10 March 2021 can now be generated upto 31 March 2021. For the documents signed from 11 March 2021 onwards, the original guidance for generation of UDIN, i.e., within 15 days of signing the documents will be applicable.
- Hon’ble Delhi ITAT in the case of Louis Dreyfus Commodities India Pvt Ltd Vs DCIT, Circle 4 (1) Quashes TP-order passed beyond 60-day limit u/s 92CA(3A) r.w.s.153(1) as it is barred by limitation- follows Hon’ble High Court ruling in case of Pfizer Healthcare.
- In response to various representations received by CBDT seeking clarification completion of pending assessment under Wealth Tax Act, 1957 in faceless manner, CBDT clarifies that notification introducing faceless assessments is applicable only for proceedings under Income Tax Act.
- The pending assessment under Wealth Tax Act, 1957 are to be completed by jurisdictional AOs through e-proceedings module.
- The Income Tax Department has issued refunds over ₹2.14 trillions to over 22.4 million taxpayers so far, this fiscal
- OECD publishes Arbitration Profiles of 30 countries adopting arbitration regime under Part VI of MLI
- Finance Bill 2021 becomes Act, after receiving President’s assent on 28 March 2021. Earlier the Bill was approved in the Parliament, after Lok Sabha passed it on 23 March 2021 while Rajya Sabha assented to it immediately on the next day i.e. on 24 March 2021
- CBDT (Foreign Tax & Tax Research Division) publishes International Tax Bulletin for March 2021
- Shri Anurag Singh Thakur, Union Minister of State for Finance & Corporate Affairs, in his response to a Parliamentary questions revealed the following:
- Direct Taxes (as on 31 March 2020)
Forum
SC
HC
ITAT
CIT(A)
Total
Pending Appeals
5,363
31,548
88,016
4,57,808
5,82,735
- A total of 1,55,965 declarations have been submitted in DTVSV Form-1 till 10 March 2021 under the ‘Vivad se Vishwas Scheme’.
- Up to 10 March 2021, total disputed tax as per actionable 1,29,119 Form-1 was ₹ 98,354 Crore. Further, payment of ₹ 53,320 Crore has been made by the taxpayers up to 10 March 2021, against the disputed tax under the Scheme.
Goods and Services Tax
GST litigation update
No penalty for non-compliance with Dynamic QR code up to 30 June 2021
With effect from 1 December 2020, B2C invoices issued by taxpayers having turnover more than INR 500 crores shall have Dynamic QR code. On 29 November 2020, Government issued a notification stating waiver of penalty under Section 125 of the Central GST Act for non-compliance with the said provision for the period from 1 December 2020 to 31 March 2021 subject to the condition that registered person complies with this requirement from 1 April 2021. Now vide Notification number 06/2021-Central Tax dated 30 March 2021 the Government has further extended this relaxation by 3 months up to 30 June 2021 subject to the condition that registered person complies with this requirement from 1 July 2021.
Supply of software license over internet classifiable as “goods” with HSN 8523; such supply to research and educational institutions attracts concessional rate of GST at 5%
Before we discuss this Ruling, it would be apposite to understand first the legal background around the issue. Supply of notified goods to public funded educational/research institutions enjoys concessional rate of GST at 5%. “Computer software” is one of the notified goods for this 5% tax benefit. The Applicant in this case M/s SPSS South Asia Pvt Ltd is an authorized reseller of IBM SPSS software in India. Applicant provides various statistical modelling software to various publicly funded research entities. Applicant provides software download link to its customer which also contains software license code. The applicant also provides a physical backup CD containing the software. The Backup copy of software is for Customers’ convenience only. At certain times, due fluctuation in bandwidth or any other technical reason, customers face difficulties in downloading the software and in that case, they can use the CD provided. Furthermore, in Government institutions and certain institutions, they prefer a CD for inventory record purpose. In terms of entry 5(c) of Schedule II to the CGST Act, 2017 viz. “temporary transfer or permitting the use or enjoyment of any intellectual property right” the Applicant classifies their supply of software license as “service” with HSN code 997331. So, they posed a question before AAR whether concessional rate of 5% GST would be applicable to their supply of software license as “service” with HSN code 997331.
The Karnataka AAR held that the supply made by the Applicant cannot be classified as “services” but the same is “supply of goods” with HSN code 8523. In arriving at this conclusion, the AAR observed that the software supplied by the Applicant is a pre-developed or pre-designed software and made available through the use of encryption keys and hence it satisfies all the conditions to cover them under the definition of “goods”. Further the Explanatory Notes to the Scheme of Classification of Services stipulates that the services of limited end-user license as part of packaged software are excluded from the SAC 997331. Hence, the Applicant’s supply is classifiable as “supply of goods” under HSN 8523 and is also eligible for concessional rate of 5% GST when supplied to research/educational institutions.
Occupational Health Check-up or Preventive Care service along with allied medical service provided to ‘Business entities’ taxable at 18%
Gujarat AAR classifies supply of ‘Occupational Health Check-up service’ (OHC) / Corporate Health Check-up Schemes i.e., nursing staff, doctors, paramedical staff on hospital’s payroll working in different corporate for providing health check-up service, ambulance facility, and allied medical services to their employees as “Human health and social care services”, in terms of Sl. No. 31 of the Notification No.11/2017- C.T.(Rate) dated 28 June 2017, and hence taxable at the rate 18%.
However, supply of medicines, surgical items, implants, consumables, and other allied items provided by the hospital through in house pharmacy & supply of food, room on rent, other services to admitted patients is a ‘composite supply’ of ‘In-Patient Healthcare Service’, which is exempted from CGST as per Notification No.12/2017-C.T. (Rate) dated 28 June 2017. Held that the hospital cannot provide health services including diagnostic, treatment surgery etc. without the help of medicines to be taken during treatment, implants and consumables used during their stay in the hospital. Only on using these medicines, consumable and implants as required and prescribed by the doctors and administered during their stay will the treatment be complete. Hence, supply of medicines, implants and consumables are natural bundled with the supply of health services.
GST not applicable on accounting entries made for the purpose of Indian Accounting requirements in BoA of Project office for salary cost of Expat Employees.
Maharashtra AAR rules that No GST is chargeable on accounting entries made for the purpose of Indian Accounting requirements in books of Project Office for salary cost of Expat Employees since Project Office established in India, is an extension of the Foreign Head Office, and thus the expat employees working in Project Office are employees of the employer i.e., the Head Office. There is a relation of employer and employee between the Project Office (extension of Foreign Head Office) and the expat employees and thus the provisions of Schedule III of the CGST Act comes into play as per which services by an employee to the employer in the course of or in relation to his employment will not be considered as a supply and therefore will not attract GST.
No GST on amounts recovered form employees towards parental insurance premium
UP AAR rules that recovery of premium amount from employees by the employer and subsequent deposit of same with insurance company cannot be treated as supply of service in the course of furtherance of business. Providing insurance facility to employees’ parents is nowhere connected with the business of the applicant in as much facilitating insurance services for employees’ parents is not an activity which is incidental or ancillary to the business activity of the applicant.
No GST on amounts recovered from employees for transport facility provided through third party vendors
UP AAR rules that providing transport facility to the employees by the employer cannot be said to be in course or furtherance of business. Arranging of transport facility for the employees and recovery from employees towards such transport facility, under the terms of the employment contract, cannot be considered as supply of service in the course of furtherance of business nor an activity which is incidental or ancillary to the business activity of the applicant. Rather, this is a facility provided to the employees under the obligation of Law of the Land. Moreover, this activity is not integrally connected to the functioning of the applicant’s business in as much the said activity is not a factor which will take their business activity forward.
CSR expenditure eligible for input tax credit
The eligibility of ITC on frees supplies given as a part of CSR activity remained a burning topic unless the UP AAR ruled that ITC in such a case is not a restricted ITC and hence can be claimed by the taxable person as an eligible ITC. It stated that CSR activities is as an essential part of the business process and thus the said are to be treated as incurred “in the course of business”.
Analyzing, the provisions as contained in section 17(5)(h) of the CGST Act, 2017, the AAR holds that the section restricts credit of the goods which were written off or disposed off by way of gift or free samples. However, free supplies given as a part of CSR activity cannot be held as a gift because the term ‘GIFT’ in common parlance would mean something which is provided to someone occasionally, without consideration and which is voluntary in nature. Free supplies made under CSR expenditure are not voluntary but obligatory as mandated under the Companies Act, 2013.
Further, the AAR also held that ITC shall not be restricted in case of goods and services being used for construction of school building which is not capitalized in the books of accounts of the taxable person.
Directorate of Revenue Intelligence is not ‘the proper officer’ under Section 28(4) Custom Act and cannot exercise power to recover duties
The issue considered by the Hon’ble Supreme Court in this case was whether the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence had authority in law to issue a show cause notice under Section 28(4) of the Act for recovery of duties allegedly not levied or paid when the goods have been cleared for import by a Deputy Commissioner of Customs who decided that the goods are exempted. In this case, a show cause notice was issued under Section 28 (4) to Canon India Private Limited alleging that the Customs Authorities had been induced to clear the cameras by willful mis-statement and suppression of facts about the cameras.
The Supreme Court has held that the officers of Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) are not ‘proper officers’ within the meaning of Section 28(4) of the Customs Act, who are empowered to undertake process or recovery of duties.
The Court observed that only an officer who did the assessment, can undertake re-assessment under Section 28 (4) of the Customs Act
Target incentive received by air travel agent is not a consideration for any service
The Larger Bench of CESTAT in a recent landmark decision in the case of Kafila Hospitality & Travels Pvt. Ltd., has held that the target incentives / Performance Linked Bonus (PLB) Commission received by air travel agents from the airlines and commission received from CRS companies is not subject to service tax under the category of Business Auxiliary Services
The Hon’ble CESTAT also held that incentives received by an assessee would not qualify as consideration towards a service as these incentives would be in relation to all supplies of an assessee, and not in relation to a particular supply. It was held that a direct correlation should be established between incentives and the activity undertaken.
Customs update
Government extends validity of Foreign Trade Policy by six months
Foreign Trade Policy 2015-2020 was originally valid for five years up to 31 March 2020. Last year, its validity was extended by one more year up to 31 March 2021. Vide Notification number 60/2015-2020 dated 31 March 2021, the Government has further extended the validity of Foreign Trade Policy 2015-2020 by another six months till 30 September 2021. FTP inter alia provides various export promotion/incentive schemes such as EPCG, Advance Authorization, EOU, STP etc. Such schemes now would continue to operate in their present form up to 30 September 2021.
No fees to update Importer Exporter Code between April-June
Readers may be aware that, last month the DGFT made it mandatory to update IEC details online every year during April-June period. Even in case there are no changes in IEC details, IEC holders are required to confirm the same online. IEC may be deactivated temporarily if it is not updated in a timely manner. Now, the DGFT has notified that no fees will be charged for annual amendment of IEC between the period April to June.
IGST exemption on imports available to EPCG, Advance Authorization holders, EOUs/STP units extended up to 31 March 2022
IGST and compensation cess exemption on imports available to EPCG, Advance Authorization holders, EOUs/STP units has been extended by the Government for another year up to March 31, 2022.
New e-customs portal notified
Government has notified new e-customs portal: https://www.icegate.gov.in to facilitate electronic filing of import export documentation, amendments to documents etc. Soon all orders, decisions, summons or notices will be uploaded on this portal.
Mandatory to file bill of entry for imports at least one day in advance of arrival of vessel
Government has made various changes in time limit to file bill of entry for home consumption or warehousing. The same are tabulated below for easy understanding. It is also worthwhile to note that importers can file their bill of entry up to 30 days in advance of expected arrival of the aircraft or vessel or vehicle. Importers are advised to file bill of entry within time to avoid late filing charges.
Customs Port
Customs sea port
Customs sea port
Airport
Inland Container Depot (ICD) or Air Fright Station (AFS)
Land Customs Station (LCS)
Countries
Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Pakistan, Sri Lanka
All countries except above
All countries
All countries
All countries
Time Limit to file Bill of Entry: At least before the end of
T day
T-1 day
T day
T-1 day
T day
T denotes day of arrival of vessel or aircraft or vehicle carrying the goods at customs sea port, airport, inland container depot, land customs station
Due Dates
Important Due Dates, March 2021
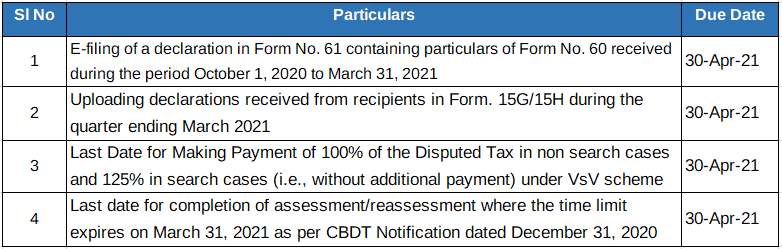
GST Compliance Calendar
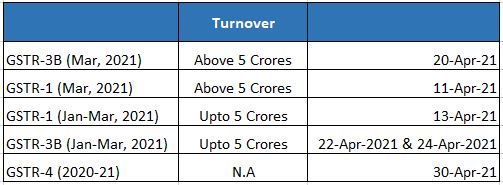
SINGAPORE UPDATES
Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) Latest Updates
1) Filing of financial statements in XBRL format and application for financial reporting reliefs under the Companies Act
From 1 May 2021, companies required to file financial statements in XBRL format must apply the revised XBRL filing requirements.
Under the revised filing requirements, non-publicly accountable companies with revenue and total assets of up to $500k can file using the Simplified XBRL template. The other companies must file using the Full XBRL template.
Companies may voluntarily file their financial statements by applying the revised XBRL filing requirements.
Other Updates
1) The Singapore- Indonesia Bilateral Investment Treaty Enters into Force
On 9 March 2021, the Minister for Trade and Industry of Singapore Chun Chun Sing and Indonesia’s Minister for Foreign Affairs Retno Marsudi (“Ministers”) jointly announced the entry into force of the Singapore -Indonesia Bilateral Investment Treaty (“BIT”) at a virtual Meeting.
The press release issued by Singapore’s Minister for Trade and Industry(“MTI”) notes that the entry into force of the BIT is an important milestone in Countries’ longstanding economic relationship. The BIT would offer greater protection for Singapore investors into the Indonesian market and vice versa, safeguarding investments and boosting investor’s confidence.
Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, Singapore continued to be Indonesia’s top source of foreign direct investment in 2020, with investment totaling US$9.8 billion, an increase from previous year. Similarly, Indonesia remained one of Singapore’s top trading partners in 2020, with bilateral trade reaching US$ 48.8 billion. The Ministers believe that the BIT could increase the bilateral investment by 18-22% over the next five years.
2) SGX RegCo allows Mainboard issuers up to 31 December 2021 to seek or renew enhanced share issue limit amid COVID-19.
On 16 March 2021, Singapore Exchange Regulation (“SGX RegCo”) announced that it has, in consultation with the Monetary Authority of Singapore, extended the availability of the provisional measure enabling Mainboard issuers to seek a general mandate for an issue of pro-rata shares and convertible securities of up to 100% of their share capital (excluding treasury shares and subsidiary holdings in each class) (“Enhanced Share Issue Limit”) as compared to the previous limit of 50%.
SGX RegCo previously announced on 8 April 2020 that the Enhanced Share Issue Limit would be in force until 31 December 2020. With SGX RegCo’s latest announcement, the expiry date of Enhanced Share Issue Limit has been extended. Issuers will have up to 31 December 2021 to seek or renew a general mandate for the Enhanced Share Issue Limit, which will expire at the conclusion of the next annual general meeting or on the date by which the next annual general meeting is required by law or the SGX-ST Mainboard Listing Manual to be held, whichever is the earliest.
IRAS- Due dates
Form C-S/C for the FY 2020 -30-November-2021
Estimated Chargeable Income (ECI) (Mar year-end)- 30-Jun-2021
GST Return January – March 2021 – 30- April-2021